In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), food is more than fuel—it is daily medicine. One of the most important dietary principles in TCM is eating warm or cooked foods, especially for digestion, energy, and mental clarity.
This idea centers around a concept known as digestive fire—the body’s ability to break down food, absorb nutrients, and turn what we eat into usable energy.
Cold or raw foods require the body to spend extra energy warming them before digestion can even begin. Over time, this drains digestive fire.
Warm foods, on the other hand:
Are easier to digest
Support nutrient absorption
Help maintain steady metabolism
Reduce bloating and stagnation
This is why TCM strongly favors soups, stews, porridges, and cooked vegetables, especially in the morning and colder months.
The Importance of Hot or Warm Foods in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Gut Health Starts in the Grocery Cart
The bottom line is this: If these foods don’t make it into your grocery cart, they won’t make it into your body either. Normalizing gut function is the most important protocol in taking back your health. And the number one way to normalize gut function you may ask? Avoid foods that feed the bad gut bacteria.
What Is Dampness in Traditional Chinese Medicine?
In TCM the environment and weather are considered integral aspects of health. Traditional Chinese Medicine theory identifies climactic factors such as wind, cold, heat, and dampness, each associated with distinct patterns of imbalance within the body. Dampness, often viewed as a Yin pathogen, is considered a common contributor to various health concerns from ezcema, IBS, joint pain and fatigue.
TCM Food Therapy
By including foods from each flavor category, TCM aims to harmonize the energies of the corresponding organs and elements in the body. This balance supports overall health and can prevent illness. Consuming a variety of colored foods is thought to nourish and balance the associated organ systems and elements. For example, eating green vegetables supports the liver and Wood energy, while consuming red foods can benefit the heart and Fire energy.
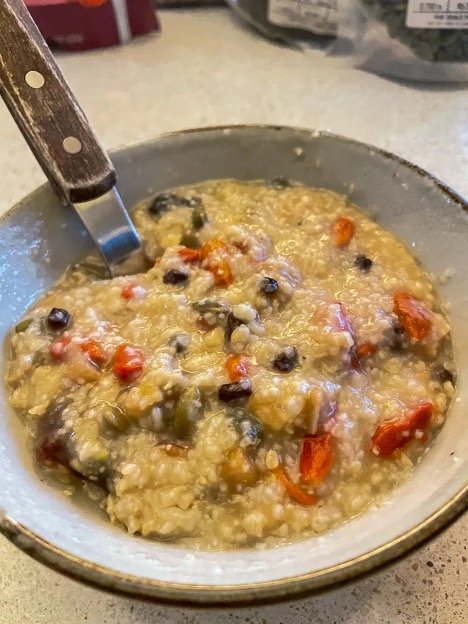
Gut Healthy Breakfast congee
Eating a gut healthy breakfast porrige is the best way to increase your digestive fire.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) the digestive flora, or microbiome relates to the Qi of the Spleen and Stomach. When SP/ST Qi become weak or deficient, symptoms like bloating, brain fog, candida overgrowth and obsessive compulsive thoughts can occur. Why? Because the inner transformation mechanism is slowed down and it takes longer for things to digest.
Reishi Mushroom (Ling Zhi): The Mushroom of Longevity
Reishi mushrooms have a long history of promoting health and longevity in East Asians countries such as China and Japan. The Latin name lucidus translates as shiny and brilliant, referring to the glossy surface of the mushroom. The name itself, Ling Zhi has a spiritual potency symbolizing success, divine spiritual energy and longevity.

Women’s Health Featured
Why Yin Matters in PeriMenopause & Beyond
Yin is the body’s cooling and nourishing foundation. It includes:
Fluids and Blood that moisten tissues and joints
Essence (Jing), our deep reserves tied to hormones and aging
The ability to rest, repair, and sleep deeply
When Yin is sufficient, we feel calm, grounded, hydrated, emotionally steady, and resilient.
Perimenopause and menopause are closely linked to the Kidney system in TCM, which governs hormones, aging, bones, and long-term vitality.
As women move into midlife, Kidney Yin naturally begins to decline. This is not a failure of the body—it’s a normal transition.
Think of it like a pond slowly receding.
When the water level drops, the sun feels hotter on the land.
In the body, this looks like less cooling Yin to balance Yang, which can create sensations of heat, dryness, and restlessness.
This stage is often called the “Second Spring” in TCM—a shift away from fertility and toward longevity, wisdom, and preservation. The key is learning how to protect and replenish Yin during this transition.
Blood Deficiency: The Hidden Root of Dry Skin, Hair Loss, & Fatigue
In TCM, Blood is one of the body’s essential substances. It works closely with Qi (energy) and plays a central role in physical strength, mental clarity, skin, emotional balance, and reproductive health.
Blood in TCM is about quality, circulation, and function, not just volume.
Blood also anchors the Shen (mind and spirit), promoting emotional stability, clear thinking, and restful sleep. In women especially, healthy Blood supports menstruation, fertility, and hormonal balance across all life stages.
Blood deficiency can look different from person to person. Common signs include:
Pale complexion or lips
Fatigue and weakness
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Dry skin, hair, or eyes
Brittle nails or hair
Poor memory or concentration
Anxiety or restlessness
Difficulty falling asleep
Numbness or tingling in limbs
Scanty, delayed, or irregular periods
Fertility challenges