In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), food is more than fuel—it is daily medicine. One of the most important dietary principles in TCM is eating warm or cooked foods, especially for digestion, energy, and mental clarity.
This idea centers around a concept known as digestive fire—the body’s ability to break down food, absorb nutrients, and turn what we eat into usable energy.
Cold or raw foods require the body to spend extra energy warming them before digestion can even begin. Over time, this drains digestive fire.
Warm foods, on the other hand:
Are easier to digest
Support nutrient absorption
Help maintain steady metabolism
Reduce bloating and stagnation
This is why TCM strongly favors soups, stews, porridges, and cooked vegetables, especially in the morning and colder months.
The Importance of Hot or Warm Foods in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Auricular Acupuncture: The Link Between Emotion, Digestion, and the Nervous System
The external ear is innervated by several nerves including the vagus nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, trigeminal nerve, facial nerve and branches of the cervical spinal nerves.
Acupuncture points on the ear are related to internal organs, carrying a parasympathetic innervation while acting as a bridge between the external ear and the internal organs.
Cupping Therapy for Muscle Recovery
Cupping therapy is a powerful yet gentle technique that supports circulation, recovery, and pain relief—making it a favorite in both traditional medicine and modern athletic care.
By improving flow and releasing deep tension, cupping helps the body recover faster and move more freely. When paired with medicated oils and skilled application, it becomes an effective tool for healing, performance, and long-term resilience.
Does Acupuncture Work? Let’s Talk Terrain, Not Magic Wands
If you’ve ever typed “Does acupuncture work?” into Google while wincing in pain, battling a stubborn symptom, or navigating fertility struggles, you’re not alone.
This question shows up in my treatment room all the time — usually followed by:
“So… will this fix me?”
“Will I be pain-free after today?”
“Can you make me pregnant?”
“Can you cure me?”
Ah, the magic wand myth.
Let’s break this down together. Acupuncture isn’t pixie dust. It’s not a one-time fix. It doesn’t “treat” disease in the conventional Western sense. What it does do — beautifully, powerfully, and consistently — is shift your terrain.
What Can Acupuncture Help With?
Explore what acupuncture treats—from chronic pain, stress, and GI issues to women’s health and neurological disorders. Book your personalized session today!
Acupuncture and Fertility
Acupuncture has been shown to positively influence the HPA axis, which plays a key role in regulating stress hormones like cortisol. By reducing stress, acupuncture helps normalize reproductive hormone levels, including estrogen and progesterone, which are critical for conception and pregnancy. Acupuncture has been found to support ovarian health by increasing blood flow to the ovaries and improving follicular development.
What to Expect at an Acupuncture Treatment
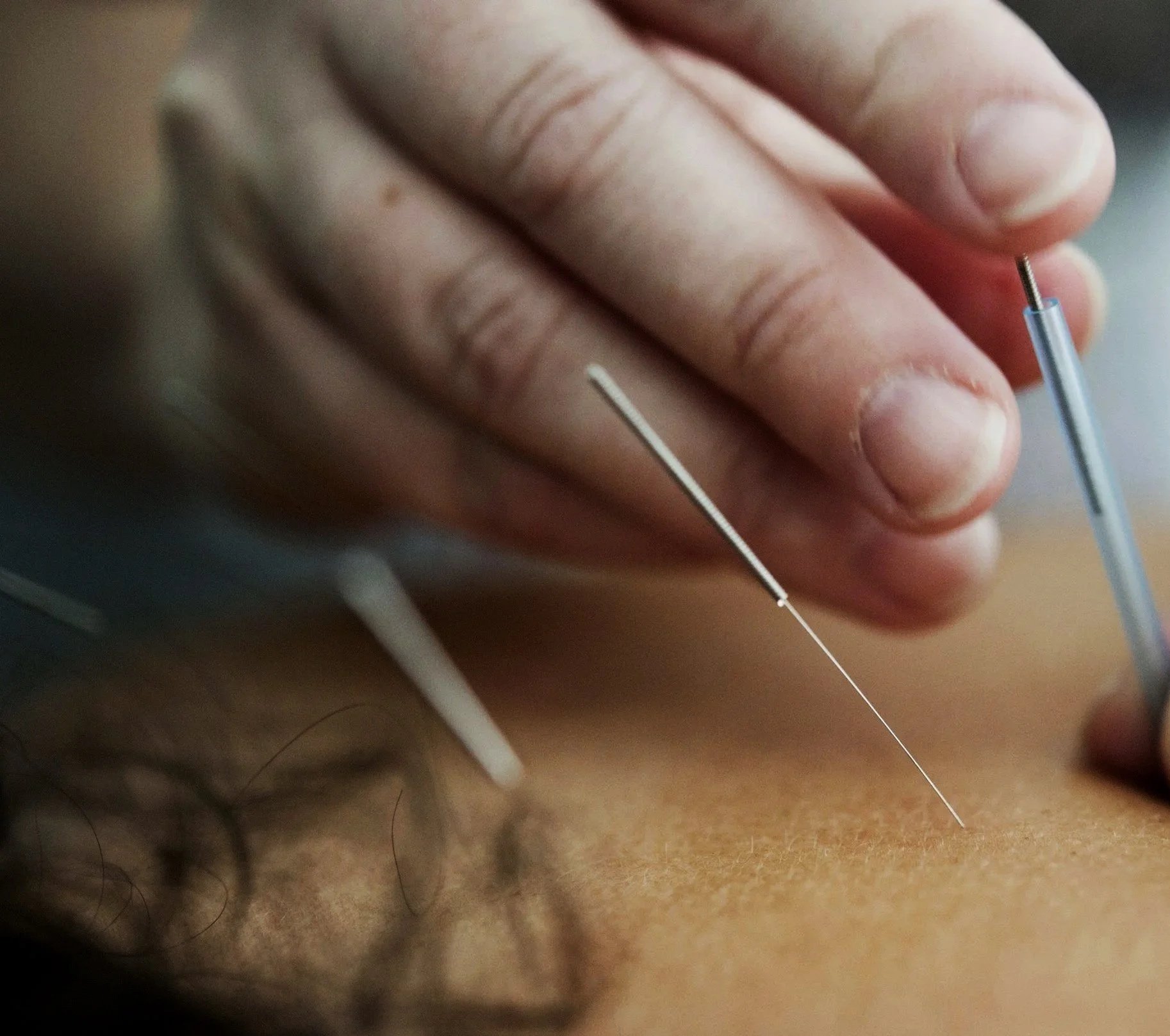
How does acupuncture work? Acupuncture regulates the Central Nervous System and its various feedback loops in the body. When acupuncture needles are inserted into an acupuncture point, it stimulates an impulse into the complex feedback mechanisms between the brain, hormones, glands and organs which are responsible for regulating all bodily processes. Acupuncture points are higsly pecific areas on the body just beyond the surface of the skin. They have high concentrations of nerve endings, mast cells, lymphatic vessels, and capillaries.

Women’s Health Featured
Why Yin Matters in PeriMenopause & Beyond
Yin is the body’s cooling and nourishing foundation. It includes:
Fluids and Blood that moisten tissues and joints
Essence (Jing), our deep reserves tied to hormones and aging
The ability to rest, repair, and sleep deeply
When Yin is sufficient, we feel calm, grounded, hydrated, emotionally steady, and resilient.
Perimenopause and menopause are closely linked to the Kidney system in TCM, which governs hormones, aging, bones, and long-term vitality.
As women move into midlife, Kidney Yin naturally begins to decline. This is not a failure of the body—it’s a normal transition.
Think of it like a pond slowly receding.
When the water level drops, the sun feels hotter on the land.
In the body, this looks like less cooling Yin to balance Yang, which can create sensations of heat, dryness, and restlessness.
This stage is often called the “Second Spring” in TCM—a shift away from fertility and toward longevity, wisdom, and preservation. The key is learning how to protect and replenish Yin during this transition.
Blood Deficiency: The Hidden Root of Dry Skin, Hair Loss, & Fatigue
In TCM, Blood is one of the body’s essential substances. It works closely with Qi (energy) and plays a central role in physical strength, mental clarity, skin, emotional balance, and reproductive health.
Blood in TCM is about quality, circulation, and function, not just volume.
Blood also anchors the Shen (mind and spirit), promoting emotional stability, clear thinking, and restful sleep. In women especially, healthy Blood supports menstruation, fertility, and hormonal balance across all life stages.
Blood deficiency can look different from person to person. Common signs include:
Pale complexion or lips
Fatigue and weakness
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Dry skin, hair, or eyes
Brittle nails or hair
Poor memory or concentration
Anxiety or restlessness
Difficulty falling asleep
Numbness or tingling in limbs
Scanty, delayed, or irregular periods
Fertility challenges